Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions. Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat. The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer.
Why Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heart beat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart.
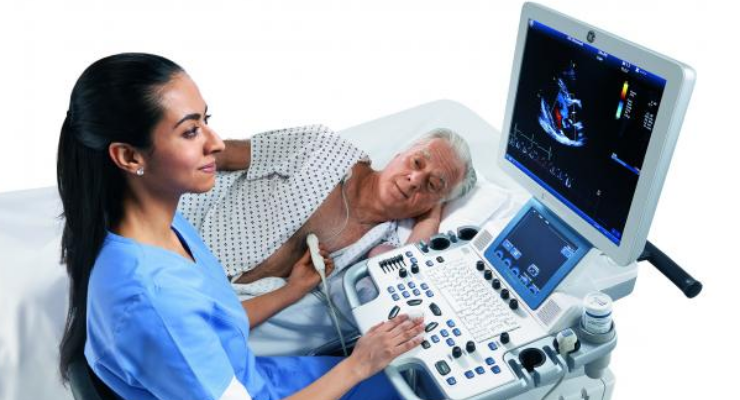
Echocardiography (ECHO)
Echocardiography is a test that uses sound waves to produce live images of your heart. The image is called an echocardiogram. This test allows your doctor to monitor how your heart and its valves are functioning. The images can help them get information about blood clots in the heart chambers.
Why Echocardiography?
An echocardiogram checks how your heart's chambers and valves are pumping blood through your heart. An echocardiogram uses ultrasound technology to see how blood moves through your heart. An echocardiogram can help doctor to diagnose heart conditions.
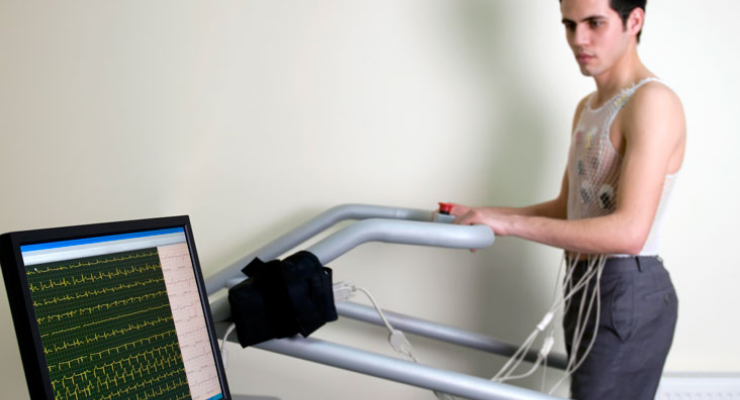

Exercise Tread Mill Test (TMT)
A Treadmill Stress Test (TMT) is a form of stress test that's conducted while you do an exercise walking on a treadmill during the course of an Electro Cardiogram (ECG). The TMT testing compares blood circulation in your heart when you're resting and under the influence of optimum physical pressure.
Why Tread Mill Test?
It helps to reveal irregular heart rhythms or other symptoms that indicate coronary artery disease, such as blocked arteries. If doctor determines you may have coronary artery disease or other heart problems, then the doctor may begin treatment or order more tests to treat the patient
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
It allows many blood pressure (BP) readings to be recorded over a 24-hour period, whether the patient is awake or asleep. At a doctor’s office or clinic, an instrument called a sphygmomanometer is used to take BP readings. Usually, only one or two readings are taken during a doctor’s visit.
Why Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring?
Ambulatory BP monitoring provides additional information about how your changes in BP may correlate with your daily activities and sleep patterns. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends confirming a diagnosis of hypertension with ambulatory BP monitoring. For most people systolic BP decreases about 10%-20% during sleep. However, for some people BP might not drop during sleep and may even rise.
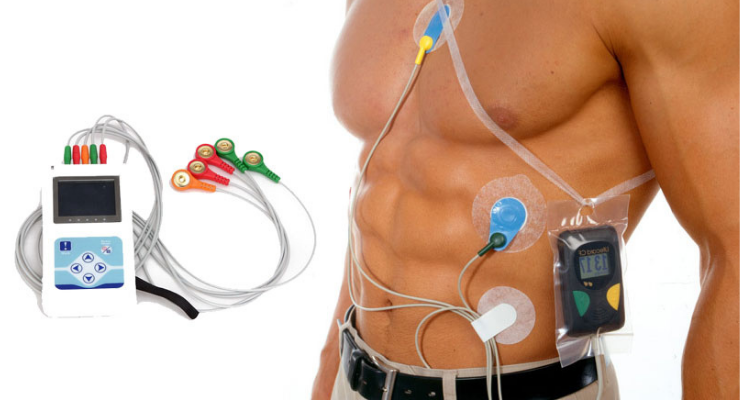
Holter (24 Hours ECG Monitoring)
In cardiology, a Holter monitor is a type of ambulatory electrocardiography device, a portable device for cardiac monitoring for at least 24 hours. The Holter's most common use is for monitoring ECG heart activity.
Why Holter Monitoring Test?
A Holter monitor test is usually performed after a traditional test to check your heart rhythm (electrocardiogram), especially if the electrocardiogram doesn't give your doctor enough information about your heart's condition. Patient with history of giddiness and syncope (loss of consciousness) and history of palpitations (hearing ones own heart beat abnormally)
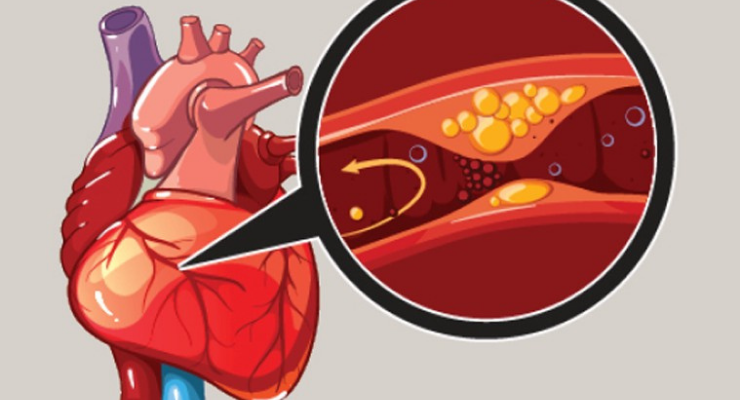
Coronary Angiography
It is a procedure that used check for blocked or narrowed blood vessels in your heart contrast dye and x ray images to detect blockages in the coronary arteries that are caused by plaque buildup. Blockages prevent your heart from getting oxygen and important nutrients.
Why Coronary Angiography?
Patient having chest pain, having indications like typical angina whose stress (TMT) has evidance of inducible ischemia or patient having heart attack require coronary angiography.
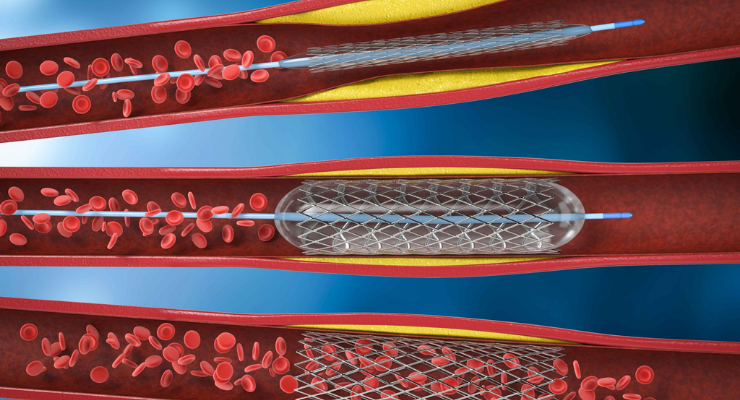
Angioplasty and Stenting
It is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called the coronary arteries. A coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that expands inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed during or immediately after angioplasty.
Why Angioplasty and Stenting?
Angioplasty can improve symptoms of blocked arteries, such as chest pain and shortness of breath. Angioplasty is also often used during a heart attack to quickly open a blocked artery and reduce the amount of damage to your heart.
Online Consultation
Incase you are unable to meet Doctor, then personally book an online consultation in Health Plix.







